LEED certification for architects or engineers is an important energy standard that can be achieved with Fabreeka thermal break.
Building standards and energy standards go hand in hand; over the years these standards evolved as requirements changed with them. Because of this change, many architects and engineers prioritize energy efficiency in their future building and construction plans.
While there is a general code or set of requirements structural engineers and architects must meet, there are a few ways to have their projects assessed for energy efficiency. As we shift towards new focuses on sustainability and energy efficiency, these certifications are higher on the priority list for engineers and architects.
Below, we discuss the LEED certification, a set of project-dependent requirements that aim to assess a project’s energy efficiency. Read on to learn more about LEED certification, thermal break and the solutions engineers and architects trust to achieve their energy efficiency goals.

What is LEED Certification?
Spearheaded by the US Green Building Council, LEED (Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design) certifications recognize best-in-class building strategies and practices for green building.
Building projects satisfy prerequisites and earn points to achieve different levels of LEED certification. Of course, how these buildings are assessed vary from project to project.
Per USBGC.gov, “LEED certification is for all building types and all building phases including new construction, interior fit outs, operations and maintenance and core and shell.”
From building design and construction to neighborhood development, LEED certification comes in all forms. You can check out the full list of certifications here. The current LEED v4.1 standard recognizes four categories of LEED certification.
The four categories include certified, silver, gold and platinum with a point threshold for each category. What might some of these requirements look like?
LEED Certification Requirements
As mentioned, there are different levels of LEED certification. Each category has its own unique technical requirements. However, the LEED certification also accounts for a general list of requirements. LEED goes into greater detail on their own website, but the requirements address everything from sustainability to occupant health.
LEED certification ensures that engineers and architects deliver high quality market practices and translate those efforts into sustainable, healthy building strategies. As you might imagine, these strategies must address anything that impacts their LEED certification. Thermal bridging, for instance, disrupts energy efficiency.
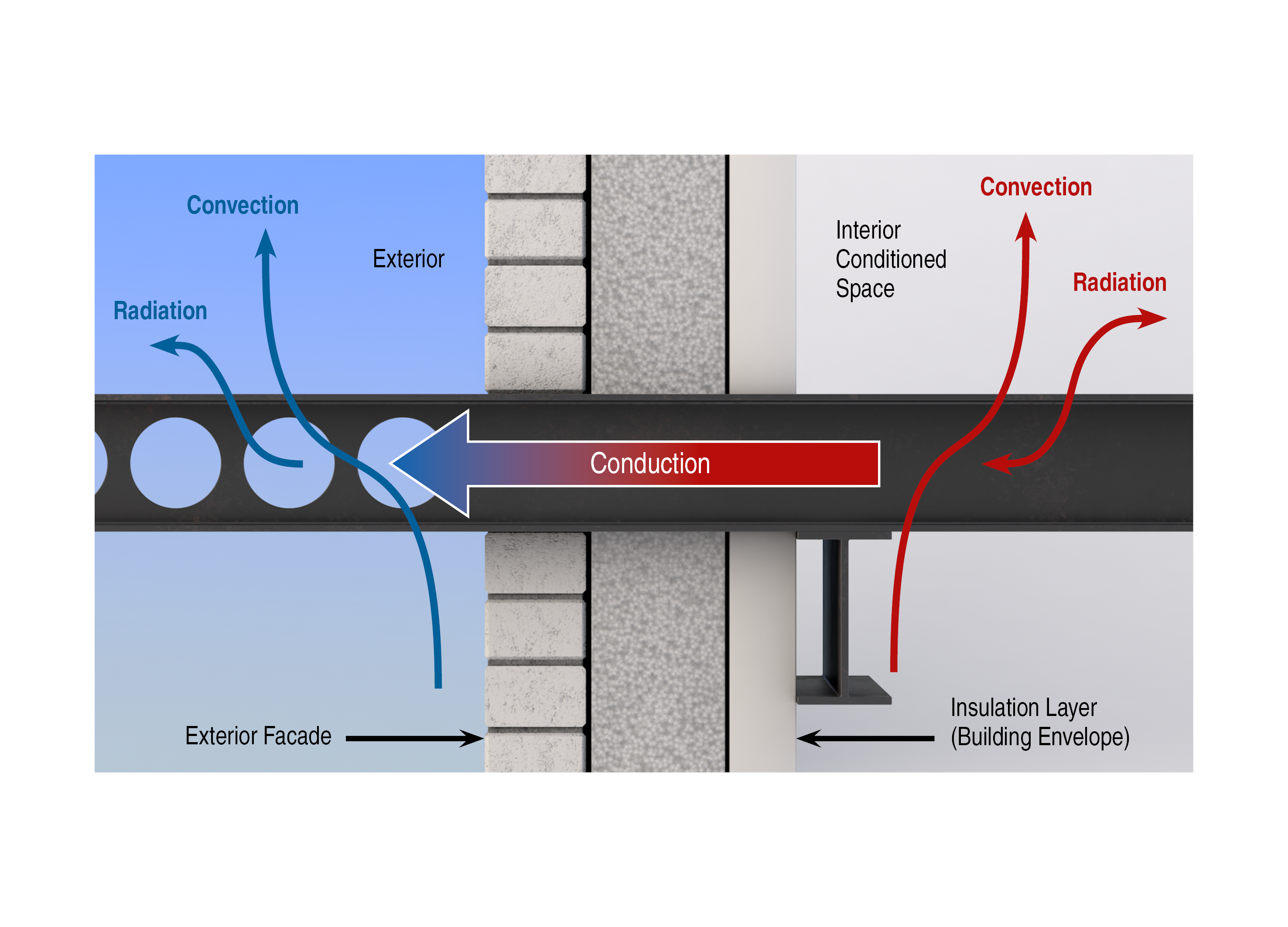
Causes, Effects, and Thermal Bridging Solutions
Structural engineers and architects have much to consider when designing building and construction projects.
Along with the many forces at play, engineers and architects must also consider energy transfer in their structures. Thermal energy transfer, specifically thermal bridging, causes buildings to become less energy efficient.
Thermal bridging occurs when conductive materials, like steel, act as a vessel for energy to transfer across a thermal barrier. This causes energy loss and potential damage from condensation. Heat looks for the path of least resistance, and therefore transfers to the colder side.
In cold climates, the heat transfers from the interior to the exterior, while that opposite happens in warm climates. However, there are thermal bridging solutions that are an effective way to maximize energy efficiency in buildings.
Structural thermal break materials prevent heat flow at transmission points throughout the structure. The material keeps heat where it is supposed to be, whether that be indoors or out. Thermal break material is an important piece of the building and construction design process. As more gravitate towards energy-efficient building design, thermal break is a must for any LEED certification.
READ NEXT ➡️ What Is The Best Thermal Break Material?
Thermal Break for LEED Certification
When it comes to innovative, energy-efficient building design, Fabreeka has the solutions to help achieve LEED certification for your project.
The effects of thermal bridging should never be an obstacle to sophisticated building design. To navigate these challenges, Fabreeka offers our line of Fabreeka-TIM® products that is specified by building professionals everywhere.
Fabreeka-TIM®
Reduce thermal energy transfer with Fabreeka-TIM. Our structural thermal break material provides thermally efficient, energy-saving results.
Manufactured from a fiberglass-reinforced laminate composite, Fabreeka-TIM is a load bearing thermal break used in between flanged steel connections including moment connections.
When used in conjunction with Fabreeka-TIM washers and Fabreeka bushings, the structural thermal break material is guaranteed to deliver energy-saving results. The complete system breaks heat flow through bolts and points of connection throughout the structure.
For your next project, strive for LEED certification with confidence as the Fabreeka-TIM provides delivers superior thermal break material.
Fabreeka-TIM® RF

Ideal for steel and concrete connections in compression, Fabreeka-TIM RF makes for another excellent thermal break solution.
Compared to its companion, Fabreeka-TIM RF boasts many of the same impressive qualities while being made from a different material.
Impermeable by any type of liquid, Fabreeka-TIM RF reduces thermal energy transfer while also resisting wear from moisture, severe weather and harsh environments.
Manufactured in an array of densities, Fabreeka-TIM RF supports a range of load conditions making resistant to varying degrees of mechanical stress.
Fabreeka-TIM® LT
Like the previous two solutions, Fabreeka-TIM LT15 material reduces thermal bridging and disrupts energy flow paths through conductive building components.
Designed for light loads, the Fabreeka-TIM LT pad improves energy efficiency and works for façade support brackets and clips to metal framing.
Compared to vinyl and plastics, the Fabreeka-TIM LT15 material provides better insulation and reduces corrosion between dissimilar metal elements.
The Latest in Thermal Bridging Solutions, All in One Place
👇👇👇
Your FREE Thermal Bridging Solutions brochure is just a few clicks away
***
Take on your next project with industry-leading solutions from Fabreeka. Our team of engineers works with you to develop a solution for your building and construction projects.
With custom-made materials for thermal break, it’s easy to see why Fabreeka is routinely specified by structural engineers and architects.






SUBMIT YOUR COMMENT